Help
Note that this help is available from within the calculator, just select Help from the main menu.
Basic Operation
Number Entry
The number keys  to
to  and decimal point
and decimal point  are used to enter numbers. To enter a negative number, press
are used to enter numbers. To enter a negative number, press  after entering the number.
after entering the number.
The  key deletes the last digit entered and can be used to correct a number or exponent.
key deletes the last digit entered and can be used to correct a number or exponent.
The  key clears the display ready for a new calculation.
key clears the display ready for a new calculation.
Exponents
To enter a number with an exponent, press  then enter the exponent using the number and
then enter the exponent using the number and  keys. Note that the exponent key means 'times 10 to the power' and it is not necessary to enter the 'times 10' yourself. The maximum exponent which can be entered is 999.
keys. Note that the exponent key means 'times 10 to the power' and it is not necessary to enter the 'times 10' yourself. The maximum exponent which can be entered is 999.
For example, to enter 2.5x1012, press:





 → 2.5x1012
→ 2.5x1012
Secondary Functions
The  key is used to access the secondary function of each key (displayed above the key in orange). While shift is active, 'SHIFT' will be shown on the display. Press
key is used to access the secondary function of each key (displayed above the key in orange). While shift is active, 'SHIFT' will be shown on the display. Press  again to cancel shift mode.
again to cancel shift mode.
As an alternative to using shift, the secondary function of each key can also be accessed by holding down the key. This feature can be disabled in Settings.
Throughout this help, functions which require shift to access are shown in orange. The shift key itself is not shown.
Keyboard Support
External hardware keyboards are supported for value entry and calculations. Each calculator function is mapped to a single key. The keyboard is used as follows:
 and the space bar for
and the space bar for  .
. (the '-' sign is only used for subtraction, not for entering negative values).
(the '-' sign is only used for subtraction, not for entering negative values).Display
Number Format
The display style can be selected between 7-segment, dot-matrix or standard font.
Numbers can be formatted on the display using either a point or a comma as the decimal separator. Numbers can also be displayed with digit grouping, using either a comma/point or space to separate groups of digits. Note that grouping with a space is not supported with the 7-segment display style, due to the fixed layout of the digits.
In decimal mode, the digit grouping can be selected between three-digit, four-digit or Indian grouping. For binary, hexadecimal or octal mode, numbers are always displayed in groups of four digits.
These options can be changed in the settings, under 'Display Format'.
Display Modes
There are four display modes for calculation results. Use the  key to cycle through the modes. The display will show 'FIX', 'SCI', 'ENG' or blank to indicate the current mode.
key to cycle through the modes. The display will show 'FIX', 'SCI', 'ENG' or blank to indicate the current mode.
Decimal Places
To set the number of decimal places in FIX mode, or the number of significant digits in SCI or ENG modes, press  . This will bring up a dialog to select the number of digits, together with the current value rounded appropriately. When the number of digits selected is fewer than the maximum available, the display will show the number of digits after the mode indicator e.g. FIX:5 or SCI:8.
. This will bring up a dialog to select the number of digits, together with the current value rounded appropriately. When the number of digits selected is fewer than the maximum available, the display will show the number of digits after the mode indicator e.g. FIX:5 or SCI:8.
Normal mode
The result is displayed as a normal floating point value if possible. If its magnitude is less than 0.0001 or larger than will fit in the display, then scientific notation is used (see SCI mode below). The number of decimal places cannot be adjusted in this mode.
FIX mode (fixed decimal point)
The result is displayed after rounding to the number of decimal places selected by  . If there is not enough room, the result may be displayed with fewer decimal places.
. If there is not enough room, the result may be displayed with fewer decimal places.
SCI mode (scientific notation)
The result is displayed in the format A x 10B, with the mantissa (A) rounded to the number of significant digits selected by  .
.
ENG mode (engineering notation)
This is the same as SCI mode, except that the exponent is set to a multiple of 3.
Note
The value used for calculations is the unrounded result stored internally, and not the rounded value shown on the display.
Copy & Paste
Tapping the display area will bring up the Clipboard menu. From here it is possible to copy the current display value, the internal value and lists of items from the memory, history or RPN stack to the device clipboard for pasting into other apps. It is also possible to paste values from the clipboard into the calculator.
History and Memory
Result History
Each time the  key is pressed, the calculation result is added to a history list.
key is pressed, the calculation result is added to a history list.
The  key presents a dialog showing the calculation result history, with the most recent results at the top. Select the required value to enter it into the calculator.
key presents a dialog showing the calculation result history, with the most recent results at the top. Select the required value to enter it into the calculator.
Up to 50 results are stored. The history can be cleared using the button at the bottom of the dialog.
Main Memory
The main memory has four dedicated function keys:
 stores the current display value into the main memory.
stores the current display value into the main memory. recalls the value stored in the main memory.
recalls the value stored in the main memory. adds the current display value to the main memory.
adds the current display value to the main memory. subtracts the current display value from the main memory.
subtracts the current display value from the main memory.Whenever a non-zero value is stored in the main memory, the letter 'M' is shown on the display.
The main memory can also be accessed via the  and
and  keys (see below).
keys (see below).
Additional Memories
There are nine additional memories which can be accessed via the  and
and  keys. These keys show a dialog with the current values stored in the main memory 'M' and the additional memories '1' to '9'. Select the appropriate value to store or recall the memory value.
keys. These keys show a dialog with the current values stored in the main memory 'M' and the additional memories '1' to '9'. Select the appropriate value to store or recall the memory value.
Memory Reset
The values stored in all the memories can be reset to zero using the button at the bottom of the store/recall dialog.
Unit Conversion
How to Convert
The current display value can be converted between different units using the  key.
key.
Zero Values
For most conversions, an original value of 0.0 will be replaced by 1.0 as a convenience to avoid converting zero to zero. This does not apply to conversions which are not a simple ratio, e.g. temperature.
Repeat Conversions
The last-used conversion can be repeated for a new value by selecting it from the top of the convert dialog.
This feature is only available in RealCalc Plus.
Notes
The unit conversions and constants are only available in decimal mode.
Basic Functions
Arithmetic Calculations
These are entered exactly as written:




 → 75.
→ 75.
Operations can be joined together:






 → 11.
→ 11.
Multiplication and division have precedence over addition and subtraction and will be performed first:





 → 7.
→ 7.
The parentheses keys can be used to override the normal precedence:







 → 9.
→ 9.
There is no limit to the number of parentheses which can be entered.
Percentage Calculations







 → 20.
→ 20.





 → 25.
→ 25.







 → 220.
→ 220.







 → 400.
→ 400.







 → 2.4
→ 2.4
Powers and Roots


 → 400.
→ 400.



 → 216.
→ 216.


 → 5.
→ 5.


 → 4.
→ 4.




 → 3.
→ 3.
Note that rational exponents with negative bases are supported for small rational powers (denominators up to 99999).









 → 16.
→ 16.
Reciprocals





 → 0.45
→ 0.45
Constants



 → 6.28318530718
→ 6.28318530718

 → 0.36787944117
→ 0.36787944117
Modulo
The modulo function calculates the remainder after division. Integer and non-integer numbers are supported. For negative numbers, the result has the same sign as the divisor.




 → 4.
→ 4.







 → 0.7
→ 0.7




 → 2.
→ 2.




 → -2.
→ -2.
Repeat Calculations
Repeat calculations can be performed without re-entering the value and function key, by pressing the operator twice. A 'K' is shown in the display to indicate that the repeat feature is active. For example:






 → 30.
→ 30.
20 is now a constant for addition:


 → 80.
→ 80.


 → 50.
→ 50.
 → 70.
→ 70.
 → 90.
→ 90.
Similarly for subtraction, multiplication and division:





 → 7.
→ 7.


 → 12.
→ 12.

 → 4.
→ 4.




 → 10.
→ 10.

 → 14.
→ 14.






 → 25.
→ 25.


 → 20.
→ 20.
The auto-repeat mode is cancelled when another operator is pressed, or when  or
or  is pressed.
is pressed.
It is also possible to enable the auto-repeat function permanently in the settings. In this case it is not necessary to press the operator twice, and there is no 'K' indicator in the display. This mode was the default operation in RealCalc prior to v2.0.
Advanced Functions
Logarithms and Exponentiation




 → 3.00071981507
→ 3.00071981507



 → 2.49968708262
→ 2.49968708262

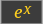 → 20.0855369232
→ 20.0855369232



 → 316.227766017
→ 316.227766017
Trigonometric Functions
For trigonometric functions, angles can be specified in degrees, radians or grads. The  key cycles through the angle modes, and the display will show DEG, RAD or GRAD to indicate the current mode.
key cycles through the angle modes, and the display will show DEG, RAD or GRAD to indicate the current mode.
The  key also cycles through the angle modes, but also converts the current value in the display.
key also cycles through the angle modes, but also converts the current value in the display.


 → 0.5
→ 0.5




 → 1.
→ 1.


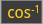 → 60.
→ 60.



 → 3.14159265359
→ 3.14159265359
Hyperbolic Functions
For hyperbolic functions press the  key before pressing
key before pressing  ,
,  or
or  . For inverse hyperbolic functions use
. For inverse hyperbolic functions use  in combination with
in combination with  . The 'HYP' indicator will appear in the display.
. The 'HYP' indicator will appear in the display.


 → 27.2899171971
→ 27.2899171971



 → 2.88727095036
→ 2.88727095036
Factorials and Permutations


 → 3,628,800.
→ 3,628,800.



 → 60.
→ 60.



 → 10.
→ 10.
Fractions & DMS
Note
Please note that Fractions and DMS are only available in RealCalc Plus.
Fractions
Fractions are entered using the  key, and can be entered as either mixed or improper fractions. The results of calculations involving fractions will be displayed as fractions where appropriate, reduced to their lowest terms.
key, and can be entered as either mixed or improper fractions. The results of calculations involving fractions will be displayed as fractions where appropriate, reduced to their lowest terms.
Fraction Calculations







 → 15/12
→ 15/12










 → -11/8
→ -11/8









 → 21/16
→ 21/16
Fraction Conversion
The  key also converts between mixed fraction, improper fraction and decimal format.
key also converts between mixed fraction, improper fraction and decimal format.




 → 0.375
→ 0.375
 → 3/8
→ 3/8




 → 211/20
→ 211/20
 → 51/20
→ 51/20
 → 2.55
→ 2.55
 key does nothing
key does nothing
 → 3.14159265359
→ 3.14159265359
Limits
The following restrictions apply to fraction entry and results:
Calculation results which do not meet these restrictions will be converted to decimal.
Degrees, Minutes and Seconds (DMS)
DMS values are entered using the  key, and can be entered as either decimal degrees, whole degrees with decimal minutes, or whole degrees and minutes with decimal seconds.
key, and can be entered as either decimal degrees, whole degrees with decimal minutes, or whole degrees and minutes with decimal seconds.
DMS Calculations












 → 4°15'20.00"
→ 4°15'20.00"















 → 4°08'48.00"
→ 4°08'48.00"
DMS Conversion
The  key also converts between DMS and decimal format.
key also converts between DMS and decimal format.




 → 1°15'00.00"
→ 1°15'00.00"
 → 1.25
→ 1.25





 → 2.5
→ 2.5
 → 2°30'00.00"
→ 2°30'00.00"
Limits
The maximum value which can be displayed as DMS is 9999°59'59.9999". Calculation results outside this range will be converted to decimal.
Binary, Octal and Hex
Changing Mode
These modes are set using the  ,
,  and
and  keys respectively. The
keys respectively. The  key returns to the normal decimal mode. The current value on the display is truncated to an integer when switching modes (alternatively, rounding to integer is available as an option in the settings).
key returns to the normal decimal mode. The current value on the display is truncated to an integer when switching modes (alternatively, rounding to integer is available as an option in the settings).
Please note that these modes are disabled by default, and can be enabled in the settings.
Number Range
When in BIN, OCT or HEX modes, calculations are performed on signed integer values up to 12 digits. Non-integer results will be truncated.
Negative values are represented in 2's, 8's or 16's complement notation.
Example:


 → -1.
→ -1.
 → 1111,1111,1111.
→ 1111,1111,1111.
 → 7777,7777,7777.
→ 7777,7777,7777.
 → FFFF,FFFF,FFFF.
→ FFFF,FFFF,FFFF.
Pressing the  key negates the current value on the display:
key negates the current value on the display:




 → 1111,1111,1001.
→ 1111,1111,1001.
 → 111.
→ 111.
Logical Operations
The following bitwise logical operations are available (all examples in HEX mode):
 - bitwise inversion
- bitwise inversion

 → FFFF,FFFF,FF8A.
→ FFFF,FFFF,FF8A.
 - bitwise logical AND
- bitwise logical AND




 → 62.
→ 62.
 - bitwise logical NAND
- bitwise logical NAND




 → FFFF,FFFF,FF9D.
→ FFFF,FFFF,FF9D.
 - bitwise logical OR
- bitwise logical OR




 → F7.
→ F7.
 - bitwise logical NOR
- bitwise logical NOR




 → FFFF,FFFF,FF08.
→ FFFF,FFFF,FF08.
 - bitwise exclusive-OR
- bitwise exclusive-OR




 → 95.
→ 95.
 - bitwise exclusive-NOR
- bitwise exclusive-NOR




 → FFFF,FFFF,FF6A.
→ FFFF,FFFF,FF6A.
Shift & Rotate Functions
The following bitwise shift and rotate functions are available (all examples in HEX mode):
 - arithmetic shift left
- arithmetic shift left





 → 1,3CD0.
→ 1,3CD0.
 - arithmetic shift right
- arithmetic shift right






 → FFFF,FFFF,FB0C.
→ FFFF,FFFF,FB0C.
 - logical shift right
- logical shift right






 → 1FFF,FFFF,FB0C.
→ 1FFF,FFFF,FB0C.
 - single-bit rotate left
- single-bit rotate left


 → FFFF,FFFF,FE01.
→ FFFF,FFFF,FE01.
 - single-bit rotate right
- single-bit rotate right

 → 8000,0000,007F.
→ 8000,0000,007F.
History and Memory Dialogs
When in BIN, OCT or HEX modes, the values in the history and memory dialogs are presented in the current mode. Values which cannot be converted to the current mode are shown as 'Error' and cannot be selected.
RPN Mode
RPN Mode
RPN mode can be enabled in the Settings (select Calculator Type > RPN).
In RPN mode, values are entered first, followed by the function key. Values are pushed onto a stack using the  key. Functions take their arguments off the bottom of the stack, and push their result back onto the stack.
key. Functions take their arguments off the bottom of the stack, and push their result back onto the stack.
RPN Styles
Three styles of RPN behaviour are supported. The style can be selected in the Settings.
1. Unlimited stack, no entry buffer.
In this mode, new values are entered directly into the X register. It is not necessary to press the ENTER key before using the value in a calculation. If ENTER is pressed, the value is placed in both X and Y, and the value in X will be replaced by a new entry. The stack size is unlimited.
The  key drops the X value off the bottom of the stack, shifting the remainder of the stack down. If the stack becomes empty, a zero remains in the X register.
key drops the X value off the bottom of the stack, shifting the remainder of the stack down. If the stack becomes empty, a zero remains in the X register.
The 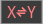 key swaps the values in the X and Y registers.
key swaps the values in the X and Y registers.
This is the original RealCalc RPN behaviour (prior to version 2.0) and is the only style supported in the free version of RealCalc.
2. Unlimited stack, with entry buffer.
In this mode, new values are entered into a separate buffer (indicated by a right-arrow on the entry line). When ENTER is pressed, the value is placed in the first register only. It is not necessary to press the ENTER key before using the value in a calculation. The stack size is unlimited, and labeled 1,2,3 rather than X,Y,Z.
The  key drops the first value off the bottom of the stack, shifting the remainder of the stack down.
key drops the first value off the bottom of the stack, shifting the remainder of the stack down.
The  key swaps the values in the X and Y registers.
key swaps the values in the X and Y registers.
(This mode is only available in RealCalc Plus).
3. Four-level XYZT stack.
In this mode, the stack size is fixed at four, labeled X,Y,Z,T. New values are entered directly into the X register. If ENTER is pressed, the value is placed in both X and Y, and the value in X will be replaced by a new entry.
When the stack drops, the value in T is copied into Z (leaving T unchanged).
The  key rolls the stack down, moving the X value back into the T register.
key rolls the stack down, moving the X value back into the T register.
The 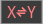 key swaps the values in the X and Y registers.
key swaps the values in the X and Y registers.
(This mode is only available in RealCalc Plus).
Stack Operations
The following additional functions are available in all RPN styles.
 key re-enters the value which was in the X register before the last operation.
key re-enters the value which was in the X register before the last operation. key opens a dialog which shows the contents of the stack.
key opens a dialog which shows the contents of the stack. key reverses the last stack operation (any entry in progress is unaffected).
key reverses the last stack operation (any entry in progress is unaffected). key clears the stack.
key clears the stack.RPN Operation
 or
or  , simply operate on X and replace it, in the same way as normal mode:
, simply operate on X and replace it, in the same way as normal mode:
 → X: 25.
→ X: 25.
 or
or  , take X and Y off the stack and put the result back:
, take X and Y off the stack and put the result back:



 → X: 6.
→ X: 6.



 → X: 256.
→ X: 256.
Note that the percent key calculates X% of Y, placing the result in X, but leaves Y unchanged.








 → X: 3.
→ X: 3.
If there are insufficient arguments on the stack for a particular operation, 'X?' and/or 'Y?' will be displayed for a short time.
Display
The size of the display can be changed to show the first one, two, three or four registers. Simply drag the display up or down to adjust, or alternatively this can be configured in the settings.
Result History
As there is no equals key, the result of every operation is added to the result history.
Customization
Unit Conversions and Constants
Please see this page for help on customizing the unit conversions and constants.
Installation
Play Store Download and Licensing Issues
Please see this page for help with common download and licensing issues.
